can a blood test detect testicular torsion|early signs of testicular torsion : bespoke Testicular torsion occurs when the testicle rotates on the spermatic cord, which brings blood to the testicle from the abdomen. If the testicle rotates several times, blood flow to . WEB39K views 7 years ago. SpongeBob sings the sucess from Luciano from the youtube "Call the Flavinho on the Whatsapp to can enter on the Stick" .more.
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEBPrevisão para 15 dias Entre-Ijuís - RS. Gráficos. 27 ter. 23°. 27°. 90%. Sol com muitas nuvens durante o dia. Períodos de nublado, com chuva a qualquer hora. Madrugada. .
testicular torsion signs on examination
Decreased blood flow to the testicle is a sign of testicular torsion. But ultrasound doesn't always detect the reduced blood flow, so the test might not rule out testicular torsion. Surgery.
testicular torsion recovery time
Testicular torsion occurs when the testicle rotates on the spermatic cord, which . Testicular torsion occurs when the testicle rotates on the spermatic cord, which brings blood to the testicle from the abdomen. If the testicle rotates several times, blood flow to .
You might get one or more of these tests to diagnose testicular torsion: Urine test (checks for an infection) An imaging test of your scrotum, usually an ultrasound that uses . Testicular torsion is a clinical diagnosis, and patients typically present with severe acute unilateral scrotal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Physical examination may reveal a high-riding. Testicular torsion is a true urologic emergency, and early identification is critical to prevent the need for testicular amputation. Ultrasound is the ideal imaging modality to .
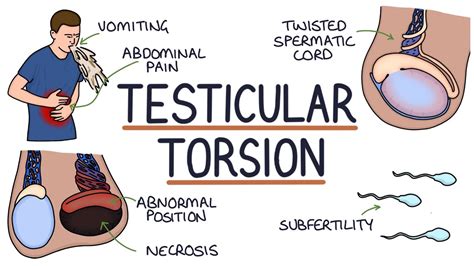
Testicular torsion is when the spermatic cord above your testicle twists, cutting off blood flow to your testicle. Testicular torsion can happen at any age, but it most often happens to boys ages .
Testicular torsion is an emergency condition due to rotation of the testis and consequent strangulation of its blood supply. Symptoms are acute scrotal pain and swelling, nausea, and vomiting. Diagnosis is based on physical . Testicular torsion is a urologic emergency caused by the twisting of the testicle on the spermatic cord leading to constriction of the vascular supply, time-sensitive ischemia, .
testicular torsion physical exam findings
testicular torsion nice guidelines
canvas test question with a multiple answer drop down
Ultrasonography. Doctors may diagnose the condition based on a description of the symptoms and the physical examination findings. Alternatively, doctors may use imaging, usually ultrasonography, for diagnosis. Treatment of Testicular .
Blood tests. Blood tests can: check your general health, including how well your liver and kidneys are working; check numbers of blood cells; help diagnose cancer and other conditions; Your blood sample is sent to the laboratory for analysis. This shows the different types of cells, chemicals and proteins in the blood.
Testicular torsion is a time-sensitive diagnosis that requires prompt surgical intervention to avoid testicular ischemia, infertility, and unwanted litigation. When imaging is required, the recommended and most available modality to detect torsion is ultrasonography. In pediatric patients, the use of SMI is supported. Introduction. Testicular torsion refers to the twisting of the spermatic cord within the scrotum. This leads to occlusion of testicular venous return and subsequent compromise of the arterial supply, resulting in .
Testicular torsion, or twisted testicle, can be extremely painful. . urine or blood tests to check for infection; testicular ultrasound to . material into the bloodstream to detect areas of . Testicular torsion occurs when a testis torts on the spermatic cord resulting in the cutting off of blood supply. The most common symptom is acute testicular pain and the most common underlying cause, a bell-clapper deformity.The diagnosis is often made clinically but if it is in doubt, an ultrasound is helpful in confirming the diagnosis.
Routine testicular self-exams can give you a greater awareness of the condition of your testicles and help you detect changes. Self-exams can also alert you to potential testicular problems. . your doctor might do a testicular exam followed by a blood test, ultrasound or biopsy. Most changes in your testicles aren't caused by testicular . It can help your provider see whether the lumps look like something that isn't cancer or if they look like cancer. An ultrasound shows whether the lumps are inside or outside the testicle. Lumps inside the testicle are more likely to be testicular cancer. Blood tests. A blood test can detect proteins made by testicular cancer cells. Testicular torsion, also termed torsion of the spermatic cord, is a relatively common and potentially devastating acute condition resulting from obstruction of the arterial blood supply to the testis. [] Fortunately, this entity is relatively well known, and it usually occurs with enough discomfort to lead to its diagnosis and subsequent testicular salvage.
The cremasteric reflex has been reported to be absent in 100% of cases of testicular torsion, making it a potentially useful sign in this diagnosis. However, a significant number of case reports and small case series exist, demonstrating that the test is not 100% specific, and the reflex can be present in cases of testicular torsion. Diagnosis of testicular torsion is based on the finding of decreased or absent blood flow on the ipsilateral side. . Physicians should order whichever test is faster and more readily available . Testicular torsion is when a testicle rotates, twisting the spermatic cord that provides it with blood and oxygen. Unless the injury is repaired within four to six hours, the loss of blood flow can irreparably damage the testicle, causing what is .
Blood tests for tumor markers. Some blood tests can help diagnose testicular tumors. Many testicular cancers make high levels of certain proteins called tumor markers, such as alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) and human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG). When these tumor markers are in the blood, it suggests that there's a testicular tumor. One of the most common tests for testicular pain is an ultrasound. This non-invasive device uses sound waves to create an image of the testicle that can detect injuries, abnormalities, nodules, and tumors. A color Doppler ultrasound can help detect blood circulation problems in cases of testicular torsion. This causes a lot of extra cells in the testicle that can form a mass called a tumor. In time, the tumor can grow beyond the testicle. Some cells might break away and spread to other parts of the body. Testicular cancer most often spreads to the lymph nodes, liver and lungs. When testicular cancer spreads, it's called metastatic testicular cancer.
Blood tests that can detect infection that could be causing your symptoms . If you have symptoms that suggest a serious condition, like testicular torsion, your doctor may recommend immediate surgical exploration to diagnose and, if possible, treat the condition.
Because extrinsic compression of the testicular parenchyma or spermatic cord can compromise inflow and outflow, one should evaluate for fluid collections around the testis and pathologic findings along the inguinal canal, .
Testicular torsion is a twisting of the spermatic cord and its contents and is a surgical emergency affecting 3.8 per 100,000 males younger than 18 years annually. It accounts for 10% to 15% of . The main tests for testicular cancer are blood tests and an ultrasound. If these tests are highly suggestive of testicular cancer, your doctor may recommend having your testicle removed.
The test can show if you have testicular torsion. Testicular torsion is a twisting of the testicle that can cut off blood flow. If ultrasound with color Doppler shows lower blood flow to a testicle than is typical, the testicle is twisted. If blood flow is higher than typical, this can help confirm that you have epididymitis.Ultrasound can often detect an absent or undescended testicle as well. It is estimated that approximately three percent of full-term baby boys have an undescended testicle. . Ultrasound can identify testicular torsion, the twisting of the spermatic cord that contains the vessels that supply blood to the testicle. Testicular torsion is caused . Testicular torsion is a urologic emergency caused by the twisting of the testicle on the spermatic cord leading to constriction of the vascular supply, time-sensitive ischemia, and/or necrosis of testicular tissue. Laher A, Ragavan S, Mehta P, et al. Testicular torsion in the emergency room: A review of detection and management strategies.
Testicular torsion is a time-sensitive diagnosis that requires prompt surgical intervention to avoid testicular ischemia, infertility, and unwanted litigation. When imaging is required, the recommended and most available modality to detect torsion is ultrasonography. In pediatric patients, the use of SMI is supported.Testicular torsion is the twisting of a testis on its spermatic cord so that the blood supply to the testis is blocked. Testicular torsion causes sudden, severe pain and later swelling of the affected testis. A doctor's examination and sometimes ultrasonography are needed for testicular torsion diagnosis. Treatment is to untwist the spermatic cord.The internal and external spermatic arteries travel through the spermatic cord to supply blood to the testicles. Testicular torsion, or the twisting of the testes on the spermatic cord, impedes this supply and is a urologic emergency. . spermatic cord and fallopian tube.13, 14 High-resolution ultrasound may detect torsion with up to 96% . Testicular trauma can happen from many things, including car and bike accidents and gunshot wounds. . Contusion: This is a bruise or a hematoma, a collection of blood beneath tissues. Testicular torsion: This means that the spermatic cord inside the testicle becomes twisted. Because the cord also has blood vessels, it must be untwisted before .
9 Testicular Torsion . David Cote. Introduction “Testicular Torsion” by Thomas Newman is licensed under CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 Testicular torsion occurs when the testicl es rotate and the spermatic cord twists. The spermatic cord brings blood flow to the scrotum; therefore, the twisting will reduce the amount of blood getting to the scrotum, which will cause severe pain and . Testicular torsion can happen to boys and men of any age, but most cases occur in boys between the ages of 12 and 18. While it’s not always known what causes torsion, some boys have what are called ‘bell-clapper testes’, where the attachments to the spermatic cord are a little bit higher than normal, making the testicle more mobile.
testicular torsion manual pdf
testicular torsion clinical signs
Resultado da 31 de mai. de 2023 · In addition, Betway offers casino and sports betting on a single platform. Plus, there are no limitations to players using Android .
can a blood test detect testicular torsion|early signs of testicular torsion